Agenda:
- Automatic differentiation
- Cross validation
- Classification
Packages we will require this week
packages <- c(
# Old packages
"ISLR2",
"dplyr",
"tidyr",
"readr",
"purrr",
"glmnet",
"caret",
"repr",
# NEW
"torch",
"mlbench"
)
# renv::install(packages)
sapply(packages, require, character.only=TRUE)Thu, Feb 23
In the last class we looked at the following numerical implementation of gradient descent in R
x <- cars$speed
y <- cars$dist# define the loss function
Loss <- function(b, x, y){
squares <- (y - b[1] - b[2] * x)^2
return( mean(squares) )
}
b <- rnorm(2)
Loss(b, cars$speed, cars$dist)[1] 1905.504This is the numerical gradient function we looked at:
# define a function to compute the gradients
grad <- function(b, Loss, x, y, eps=1e-5){
b0_up <- Loss( c(b[1] + eps, b[2]), x, y)
b0_dn <- Loss( c(b[1] - eps, b[2]), x, y)
b1_up <- Loss( c(b[1], b[2] + eps), x, y)
b1_dn <- Loss( c(b[1], b[2] - eps), x, y)
grad_b0_L <- (b0_up - b0_dn) / (2 * eps)
grad_b1_L <- (b1_up - b1_dn) / (2 * eps)
return( c(grad_b0_L, grad_b1_L) )
}
grad(b, Loss, cars$speed, cars$dist)[1] -73.13359 -1319.66565The gradient descent implementation is below:
steps <- 9999
L_numeric <- rep(Inf, steps)
eta <- 1e-4
b_numeric <- rep(0.0, 2)
for (i in 1:steps){
b_numeric <- b_numeric - eta * grad(b_numeric, Loss, cars$speed, cars$dist)
L_numeric[i] <- Loss(b_numeric, cars$speed, cars$dist)
if(i %in% c(1:10) || i %% 1000 == 0){
cat(sprintf("Iteration: %s\t Loss value: %s\n", i, L_numeric[i]))
}
}Iteration: 1 Loss value: 2266.69206282174
Iteration: 2 Loss value: 2059.23910669384
Iteration: 3 Loss value: 1873.22918303142
Iteration: 4 Loss value: 1706.44585378992
Iteration: 5 Loss value: 1556.90178087535
Iteration: 6 Loss value: 1422.815045446
Iteration: 7 Loss value: 1302.58791495713
Iteration: 8 Loss value: 1194.78780492565
Iteration: 9 Loss value: 1098.13020855732
Iteration: 10 Loss value: 1011.46339084888
Iteration: 1000 Loss value: 258.373721118606
Iteration: 2000 Loss value: 257.10759589046
Iteration: 3000 Loss value: 255.892681655669
Iteration: 4000 Loss value: 254.726907082124
Iteration: 5000 Loss value: 253.608284616954
Iteration: 6000 Loss value: 252.534907097824
Iteration: 7000 Loss value: 251.504944501478
Iteration: 8000 Loss value: 250.516640823636
Iteration: 9000 Loss value: 249.568311085141options(repr.plot.width=12, repr.plot.height=7)
par(mfrow=c(1, 2))
plot(x, y)
abline(b_numeric, col="red")
plot(L_numeric, type="l", col="dodgerblue")
Automatic differentiation
The cornerstone of modern machine learning and data-science is to be able to perform automatic differentiation, i.e., being able to compute the gradients for any function without the need to solve tedious calculus problems. For the more advanced parts of the course (e.g., neural networks), we will be using automatic differentiation libraries to perform gradient descent.
While there are several libraries for performing these tasks, we will be using the pyTorch library for this. The installation procedure can be found here
The basic steps are:
renv::install("torch")
library(torch)
torch::install_torch()Example 1:
x <- torch_randn(c(5, 1), requires_grad=TRUE)
xtorch_tensor
-0.0658
0.9932
0.2550
0.9097
-1.1083
[ CPUFloatType{5,1} ][ requires_grad = TRUE ]f <- function(x){
torch_norm(x)^10
}
y <- f(x)
ytorch_tensor
291.718
[ CPUFloatType{} ][ grad_fn = <PowBackward0> ]y$backward()\[ \frac{dy}{dx} \]
x$gradtorch_tensor
-61.7160
931.1658
239.0168
852.8220
-1039.0062
[ CPUFloatType{5,1} ](5 * torch_norm(x)^8) * (2 * x)torch_tensor
-61.7160
931.1658
239.0168
852.8220
-1039.0062
[ CPUFloatType{5,1} ][ grad_fn = <MulBackward0> ]Example 2:
x <- torch_randn(c(10, 1), requires_grad=T)
y <- torch_randn(c(10, 1), requires_grad=T)
c(x, y)[[1]]
torch_tensor
0.5419
-2.0761
-1.2139
-0.5452
-0.9114
0.1124
0.7301
0.5995
-0.8506
0.3153
[ CPUFloatType{10,1} ][ requires_grad = TRUE ]
[[2]]
torch_tensor
0.2530
-1.1521
-0.7859
0.9707
0.3526
0.7097
0.2911
-0.9521
0.7741
-0.7462
[ CPUFloatType{10,1} ][ requires_grad = TRUE ]f <- function(x, y){
sum(x * y)
}
z <- f(x, y)
ztorch_tensor
1.46023
[ CPUFloatType{} ][ grad_fn = <SumBackward0> ]z$backward()c(x$grad, y$grad)[[1]]
torch_tensor
0.2530
-1.1521
-0.7859
0.9707
0.3526
0.7097
0.2911
-0.9521
0.7741
-0.7462
[ CPUFloatType{10,1} ]
[[2]]
torch_tensor
0.5419
-2.0761
-1.2139
-0.5452
-0.9114
0.1124
0.7301
0.5995
-0.8506
0.3153
[ CPUFloatType{10,1} ]c(x - y$grad, y - x$grad)[[1]]
torch_tensor
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
[ CPUFloatType{10,1} ][ grad_fn = <SubBackward0> ]
[[2]]
torch_tensor
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
[ CPUFloatType{10,1} ][ grad_fn = <SubBackward0> ]Example 3:
x <- torch_tensor(cars$speed, dtype = torch_float())
y <- torch_tensor(cars$dist, dtype = torch_float())
plot(x, y)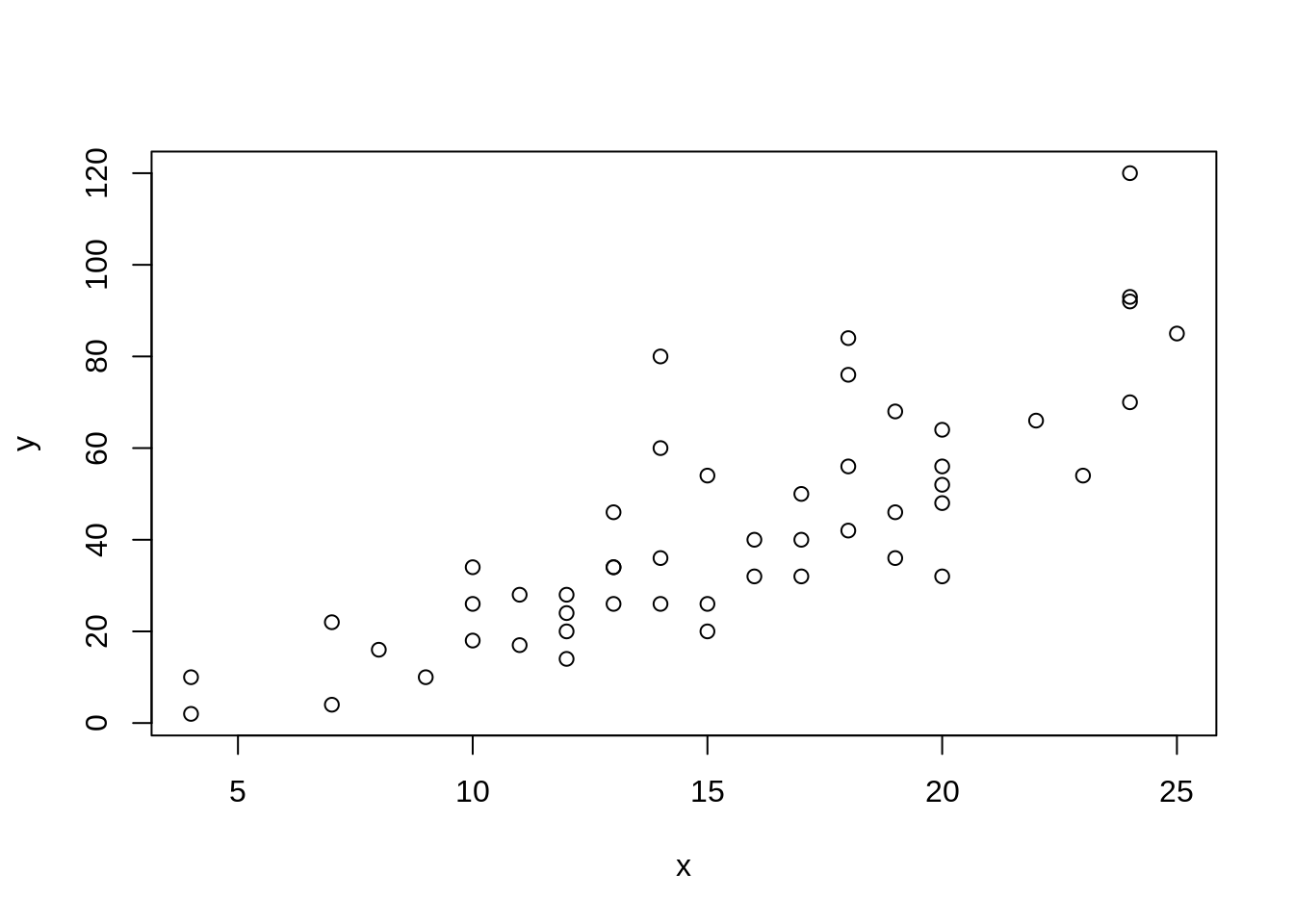
b <- torch_zeros(c(2,1), dtype=torch_float(), requires_grad = TRUE)
btorch_tensor
0
0
[ CPUFloatType{2,1} ][ requires_grad = TRUE ]loss <- nn_mse_loss()b <- torch_zeros(c(2,1), dtype=torch_float(), requires_grad = TRUE) # Initializing variables
steps <- 10000 # Specifying the number of optimization steps
L <- rep(Inf, steps) # Keeping track of the loss
eta <- 0.5 # Specifying the learning rate and the optimizer
optimizer <- optim_adam(b, lr=eta)
# Gradient descent optimization over here
for (i in 1:steps){
y_hat <- x * b[2] + b[1]
l <- loss(y_hat, y)
L[i] <- l$item()
optimizer$zero_grad()
l$backward()
optimizer$step()
if(i %in% c(1:10) || i %% 200 == 0){
cat(sprintf("Iteration: %s\t Loss value: %s\n", i, L[i]))
}
}Iteration: 1 Loss value: 2498.06005859375
Iteration: 2 Loss value: 1759.53002929688
Iteration: 3 Loss value: 1174.45300292969
Iteration: 4 Loss value: 742.353759765625
Iteration: 5 Loss value: 457.703643798828
Iteration: 6 Loss value: 307.684936523438
Iteration: 7 Loss value: 270.263397216797
Iteration: 8 Loss value: 314.067993164062
Iteration: 9 Loss value: 401.761566162109
Iteration: 10 Loss value: 496.908325195312
Iteration: 200 Loss value: 231.474166870117
Iteration: 400 Loss value: 227.11474609375
Iteration: 600 Loss value: 227.070495605469
Iteration: 800 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 1000 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 1200 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 1400 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 1600 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 1800 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 2000 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 2200 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 2400 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 2600 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 2800 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 3000 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 3200 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 3400 Loss value: 227.070388793945
Iteration: 3600 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 3800 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 4000 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 4200 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 4400 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 4600 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 4800 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 5000 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 5200 Loss value: 227.132614135742
Iteration: 5400 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 5600 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 5800 Loss value: 227.071762084961
Iteration: 6000 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 6200 Loss value: 227.093811035156
Iteration: 6400 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 6600 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 6800 Loss value: 227.070877075195
Iteration: 7000 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 7200 Loss value: 227.070617675781
Iteration: 7400 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 7600 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 7800 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 8000 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 8200 Loss value: 227.076507568359
Iteration: 8400 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 8600 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 8800 Loss value: 227.071090698242
Iteration: 9000 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 9200 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 9400 Loss value: 227.070404052734
Iteration: 9600 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 9800 Loss value: 227.070434570312
Iteration: 10000 Loss value: 229.465744018555options(repr.plot.width=12, repr.plot.height=7)
par(mfrow=c(1, 2))
plot(x, y)
abline(as_array(b), col="red")
plot(L, type="l", col="dodgerblue")
plot(L_numeric[1:100], type="l", col="red")
lines(L[1:100], col="blue")
Cross validation
df <- Boston %>% drop_na()
head(df) crim zn indus chas nox rm age dis rad tax ptratio lstat medv
1 0.00632 18 2.31 0 0.538 6.575 65.2 4.0900 1 296 15.3 4.98 24.0
2 0.02731 0 7.07 0 0.469 6.421 78.9 4.9671 2 242 17.8 9.14 21.6
3 0.02729 0 7.07 0 0.469 7.185 61.1 4.9671 2 242 17.8 4.03 34.7
4 0.03237 0 2.18 0 0.458 6.998 45.8 6.0622 3 222 18.7 2.94 33.4
5 0.06905 0 2.18 0 0.458 7.147 54.2 6.0622 3 222 18.7 5.33 36.2
6 0.02985 0 2.18 0 0.458 6.430 58.7 6.0622 3 222 18.7 5.21 28.7dim(df)[1] 506 13Split the data into training (80%) and testing sets (20%)
k <- 5
fold <- sample(1:nrow(df), nrow(df)/2)
fold [1] 293 386 154 432 137 414 122 297 279 358 161 210 262 78 501 187 32 342
[19] 352 356 29 257 441 268 368 6 497 367 458 84 176 185 301 332 30 377
[37] 366 428 437 28 334 296 448 15 286 335 304 13 90 218 430 41 139 449
[55] 395 372 383 243 42 57 115 435 485 411 53 294 207 132 40 355 99 394
[73] 254 148 204 16 105 65 413 136 461 88 4 374 134 329 172 399 290 457
[91] 217 128 17 126 70 129 475 46 145 278 498 431 322 506 35 385 74 10
[109] 267 223 429 311 3 260 310 434 375 405 338 79 95 282 505 178 188 490
[127] 440 283 2 459 306 436 83 504 488 302 247 133 447 384 138 155 31 433
[145] 307 424 114 152 331 264 249 234 277 419 191 116 170 184 392 208 76 168
[163] 406 484 61 382 427 422 12 420 158 444 321 303 50 98 248 493 209 164
[181] 96 34 270 190 242 87 91 232 465 147 480 390 350 495 120 489 107 21
[199] 452 227 146 261 318 393 23 412 341 333 47 287 144 362 82 8 166 378
[217] 142 246 285 89 199 460 320 387 179 280 67 416 68 486 400 48 453 487
[235] 86 103 325 423 229 173 253 127 494 344 481 212 312 244 327 503 62 492
[253] 346train <- df %>% slice(-fold)
test <- df %>% slice(fold)nrow(test) + nrow(train) - nrow(df)[1] 0model <- lm(medv ~ ., data = train)
summary(model)
Call:
lm(formula = medv ~ ., data = train)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-16.3877 -2.9993 -0.6342 2.2937 24.9728
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 42.204537 7.617235 5.541 7.91e-08 ***
crim -0.116032 0.052959 -2.191 0.029416 *
zn 0.060689 0.020421 2.972 0.003260 **
indus 0.024005 0.089484 0.268 0.788728
chas 3.102953 1.166564 2.660 0.008343 **
nox -21.184909 5.647907 -3.751 0.000221 ***
rm 3.737666 0.636914 5.868 1.45e-08 ***
age 0.006700 0.019316 0.347 0.728998
dis -1.834949 0.306863 -5.980 8.05e-09 ***
rad 0.306802 0.104873 2.925 0.003769 **
tax -0.013564 0.005659 -2.397 0.017297 *
ptratio -0.832380 0.202631 -4.108 5.48e-05 ***
lstat -0.611115 0.074286 -8.227 1.23e-14 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 4.992 on 240 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.7375, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7244
F-statistic: 56.2 on 12 and 240 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16y_test <- predict(model, newdata = test)mspe <- mean((test$medv - y_test)^2)
mspe[1] 21.88489k-Fold Cross Validation
k <- 5
folds <- sample(1:k, nrow(df), replace=T)
folds [1] 4 4 5 5 1 4 3 5 2 3 3 1 3 3 4 5 1 5 2 4 3 4 4 2 2 5 5 4 3 4 3 5 5 2 3 3 4
[38] 2 4 5 4 4 1 3 3 5 3 5 5 3 5 3 5 5 5 4 1 4 4 3 1 1 5 3 4 2 2 2 3 2 4 4 4 1
[75] 5 4 4 1 2 4 2 2 5 1 3 4 1 4 2 4 1 2 1 4 4 4 4 2 2 1 4 5 2 2 2 3 2 3 5 4 3
[112] 5 4 1 4 2 1 4 2 5 5 4 5 4 5 4 3 2 2 4 2 3 4 1 2 1 4 5 2 2 3 3 5 5 1 4 2 1
[149] 5 5 5 2 4 5 5 3 4 5 2 3 3 5 4 4 2 1 5 2 5 1 1 5 2 4 1 4 3 4 3 1 4 1 1 2 1
[186] 1 2 5 5 1 5 3 4 5 3 5 1 5 4 4 3 2 3 5 1 2 5 4 1 4 4 4 2 5 1 5 1 4 4 1 3 4
[223] 1 5 5 2 2 5 3 1 3 4 3 5 3 1 3 4 2 2 4 3 3 2 5 4 3 4 3 3 5 5 2 4 4 1 5 4 4
[260] 5 3 4 5 2 1 4 4 5 3 2 2 5 3 3 3 5 3 2 5 4 2 3 2 3 1 4 3 5 1 2 1 4 3 4 1 5
[297] 3 2 4 3 4 5 2 5 4 5 5 5 5 4 2 1 2 2 3 2 3 5 1 4 2 3 1 2 2 1 5 2 2 4 3 2 1
[334] 5 3 1 2 1 1 2 2 5 1 1 1 5 5 1 4 5 2 2 2 5 4 5 3 5 4 1 4 1 4 5 5 5 5 2 3 5
[371] 3 4 3 1 2 2 5 4 1 1 2 2 4 1 5 5 5 5 4 4 2 3 4 5 2 2 1 3 3 4 1 3 4 4 2 4 1
[408] 3 3 1 5 4 1 3 4 3 5 2 5 1 4 3 5 1 4 1 5 4 4 1 5 4 2 1 2 5 2 5 3 4 4 3 5 1
[445] 4 3 1 3 4 2 2 2 2 3 2 4 1 1 2 1 2 3 5 5 2 4 5 2 2 5 1 2 5 3 2 1 1 2 4 2 4
[482] 2 3 4 2 1 1 4 2 3 4 4 4 4 2 4 5 1 1 4 3 5 4 4 1 2df_folds <- list()
for(i in 1:k){
df_folds[[i]] <- list()
df_folds[[i]]$train = df[which(folds != i), ]
df_folds[[i]]$test = df[which(folds == i), ]
}nrow(df_folds[[2]]$train) + nrow(df_folds[[2]]$test) - nrow(df)[1] 0nrow(df_folds[[3]]$train) + nrow(df_folds[[4]]$test) - nrow(df)[1] 36kfold_mspe <- c()
for(i in 1:k){
model <- lm(medv ~ ., df_folds[[i]]$train)
y_hat <- predict(model, df_folds[[i]]$test)
kfold_mspe[i] <- mean((y_hat - df_folds[[i]]$test$medv)^2)
}
kfold_mspe[1] 20.10639 20.42061 34.82972 22.01352 27.47805# mean(kfold_mspe)Wrapped in a function
make_folds <- function(df, k){
folds <- sample(1:k, nrow(df), replace=T)
df_folds <- list()
for(i in 1:k){
df_folds[[i]] <- list()
df_folds[[i]]$train = df[which(folds != i), ]
df_folds[[i]]$test = df[which(folds == i), ]
}
return(df_folds)
}cv_mspe <- function(formula, df_folds){
kfold_mspe <- c()
for(i in 1:length(df_folds)){
model <- lm(formula, df_folds[[i]]$train)
y_hat <- predict(model, df_folds[[i]]$test)
kfold_mspe[i] <- mean((y_hat - df_folds[[i]]$test$medv)^2)
}
return(mean(kfold_mspe))
}cv_mspe(medv ~ ., df_folds)[1] 24.96966cv_mspe(medv ~ 1, df_folds)[1] 84.61416Using thecaret package
Define the training control for cross validation
ctrl <- trainControl(method = "cv", number = 5)model <- train(medv ~ ., data = df, method = "lm", trControl = ctrl)
summary(model)
Call:
lm(formula = .outcome ~ ., data = dat)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-15.1304 -2.7673 -0.5814 1.9414 26.2526
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 41.617270 4.936039 8.431 3.79e-16 ***
crim -0.121389 0.033000 -3.678 0.000261 ***
zn 0.046963 0.013879 3.384 0.000772 ***
indus 0.013468 0.062145 0.217 0.828520
chas 2.839993 0.870007 3.264 0.001173 **
nox -18.758022 3.851355 -4.870 1.50e-06 ***
rm 3.658119 0.420246 8.705 < 2e-16 ***
age 0.003611 0.013329 0.271 0.786595
dis -1.490754 0.201623 -7.394 6.17e-13 ***
rad 0.289405 0.066908 4.325 1.84e-05 ***
tax -0.012682 0.003801 -3.337 0.000912 ***
ptratio -0.937533 0.132206 -7.091 4.63e-12 ***
lstat -0.552019 0.050659 -10.897 < 2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 4.798 on 493 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.7343, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7278
F-statistic: 113.5 on 12 and 493 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16predictions <- predict(model, df)caret for LASSO
Bias-variance tradeoff
ctrl <- trainControl(method = "cv", number = 5)
# Define the tuning grid
grid <- expand.grid(alpha = 1, lambda = seq(0, 0.1, by = 0.001))
# Train the model using Lasso regression with cross-validation
lasso_fit <- train(
medv ~ .,
data = df,
method = "glmnet",
trControl = ctrl,
tuneGrid = grid,
standardize = TRUE,
family = "gaussian"
)
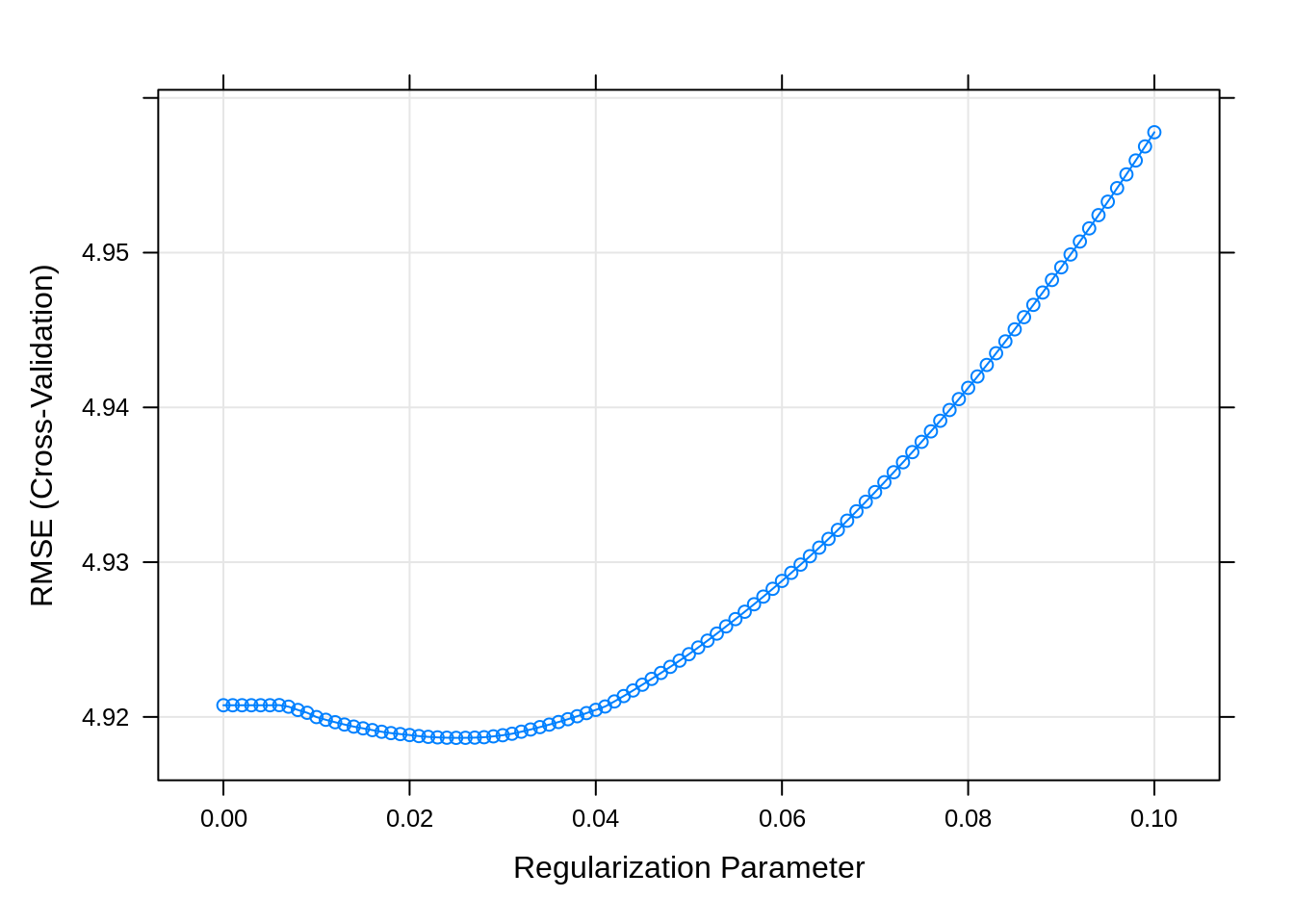
plot(lasso_fit)